
Introduction

Heart health is crucial for overall well-being. As the cardiovascular system is responsible for circulating blood throughout the body, ensuring that your heart stays healthy can lead to a longer, more active life. This blog will cover the importance of heart health, common heart conditions, risk factors, and practical tips for maintaining a healthy heart.
Understanding the Heart
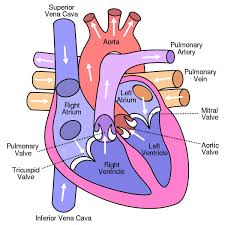
The heart is a muscular organ about the size of a fist, located slightly left of center in the chest. Its primary function is to pump blood, supplying oxygen and nutrients to tissues while removing waste products. Understanding how the heart works can help you appreciate why heart health is so important.
The Heart's Structure
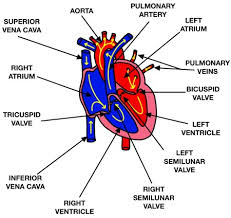
Chambers: The heart has four chambers: two atria (upper chambers) and two ventricles (lower chambers). Blood flows from the body into the right atrium, then into the right ventricle, which pumps it to the lungs. From the lungs, oxygenated blood returns to the left atrium, moves into the left ventricle, and is then pumped out to the rest of the body.
Valves: Heart valves ensure unidirectional blood flow. The mitral and tricuspid valves control blood flow from the atria to the ventricles, while the aortic and pulmonary valves regulate blood flow out of the heart.
Electrical System: The heart has its own electrical system, which controls the heartbeat. The sinoatrial (SA) node, known as the heart’s natural pacemaker, initiates each heartbeat.
Importance of Heart Health

Maintaining heart health is vital for several reasons:
Prevention of Disease: Heart disease is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. By taking care of your heart, you reduce the risk of conditions like coronary artery disease, heart attacks, and strokes.
Enhanced Quality of Life: A healthy heart improves your energy levels, mood, and overall quality of life. It allows you to engage in physical activities and enjoy time with loved ones.
Financial Savings: Preventing heart disease can also save money on medical bills and treatments.
Common Heart Conditions
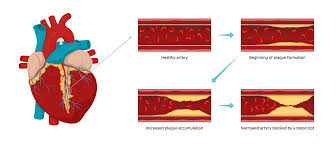
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): CAD occurs when the coronary arteries become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup, reducing blood flow to the heart muscle. Symptoms may include chest pain and shortness of breath.
Heart Attack: A heart attack happens when blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked. This can cause damage to the heart muscle and is often the result of CAD.
Heart Failure: Heart failure occurs when the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. It can result from various conditions, including CAD and high blood pressure.
Arrhythmias: These are irregular heartbeats caused by problems in the heart’s electrical system. Some arrhythmias are harmless, while others can be serious.
Valvular Heart Disease: This condition involves damage to one or more of the heart valves, affecting blood flow through the heart.
Risk Factors for Heart Disease
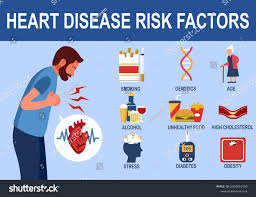
Understanding the risk factors for heart disease can help you make informed lifestyle choices:
Unhealthy Diet: Diets high in saturated fats, trans fats, sodium, and sugar can contribute to heart disease.
Lack of Physical Activity: Sedentary lifestyles increase the risk of obesity, high blood pressure, and heart disease.
Obesity: Excess body weight puts additional strain on the heart and increases the risk of conditions like diabetes.
Smoking: Tobacco use is a significant risk factor for heart disease, as it damages blood vessels and reduces oxygen in the blood.
High Blood Pressure: Hypertension can cause the heart to work harder, leading to damage over time.
High Cholesterol: Elevated cholesterol levels can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries, increasing the risk of CAD.
Diabetes: Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease due to high blood sugar levels that can damage blood vessels.
Family History: A family history of heart disease can increase your risk.
Age and Gender: Aging increases risk, and men generally face a higher risk at a younger age compared to women.
Tips for Maintaining Heart Health

Eat a Heart-Healthy Diet:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Aim for at least five servings a day. They are rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
- Whole Grains: Choose whole grain bread, pasta, and rice over refined grains.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporate sources of healthy fats, like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, while limiting saturated and trans fats.
- Lean Proteins: Opt for lean meats, fish, beans, and legumes.
- Limit Salt and Sugar: Reduce sodium intake to manage blood pressure and limit added sugars to prevent weight gain.
Stay Active:
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity each week. Activities can include walking, cycling, swimming, or dancing.
- Include strength training exercises at least twice a week to improve muscle strength and metabolism.
Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Monitor your body weight and body mass index (BMI). Losing even a small amount of weight can improve heart health.
Quit Smoking:
- If you smoke, seek support to quit. Avoid secondhand smoke as well, as it can harm your heart health.
Manage Stress:
- Chronic stress can negatively impact heart health. Engage in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
Regular Check-ups:
- Regular health screenings can help monitor blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar levels. Early detection of issues can lead to timely interventions.
Limit Alcohol Intake:
- If you consume alcohol, do so in moderation. For women, this means up to one drink per day; for men, up to two drinks.
Stay Hydrated:
- Drinking plenty of water is essential for overall health. It helps maintain blood volume and regulate body temperature.
Get Enough Sleep:
- Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Poor sleep is linked to various health issues, including heart disease.
Conclusion

Heart health is a vital aspect of overall well-being that deserves attention and care. By understanding the structure of the heart, the importance of heart health, common conditions, risk factors, and practical tips for maintenance, you can take charge of your cardiovascular health. Making informed lifestyle choices, staying active, and managing stress will go a long way in ensuring a strong and healthy heart. Remember, it’s never too late to start making changes that can positively impact your heart health.
